A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Select the first letter of the word you are seeking from the list above
to jump to the appropriate section of the glossary or scroll down to it
- A -
- affinity

- a kinship link created by marriage, such as the bond between a man and his wife and her family (in-laws). People who have an affinity relationship with each other are "affines." See consanguinity.
-
agnatic
 descent
descent - see patrilineal descent.
-
ambilineal
 descent
descent - a form of cognatic descent in which individuals can select to trace descent either matrilineally or patrilineally. The decision may be made each generation based on the relative wealth and/or importance of the father's and the mother's family lines.
-
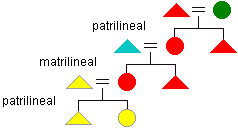
- ancestor focused kindred
- a kindred in which the person to whom all members trace their kinship ties is dead. An example would be the descendants of a well known pioneer family. It is rare for a kindred to continue functioning as an effective kin group after the death of the individual who was its focus. This usually occurs only when the ancestor was historically important.
Back to Top
- B -
-
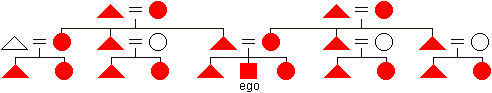
bilateral
 descent
descent - the cognatic pattern of descent in which every biological ancestor and descendant is a socially recognized relative. Everyone is a member of both his or her father's and mother's families. This is not the same as bilineal descent.
-
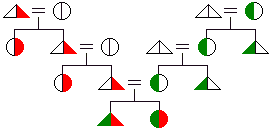
bilineal
 descent
descent - the cognatic pattern of descent in which an individual is both a member of his mother's matrilineage and his father's patrilineage. Also known as "double descent." This is not the same as bilateral descent.
-
- bride price
things of high value given by a groom to his bride's father. It is a way of showing respect for the bride and her parents. At the same time, it is a compensation for the bride's family for the loss of her economic services. It is also a way of validating the groom's right to future offspring. Bride price is most common among polygynous, small-scale, patrilineal societies--especially in sub-Saharan Africa and among Native Americans. Bride price is also referred to as "bride wealth" and "progeny price." See dowry.
Back to Top
- C -
- clan

- a group of people who claim unilineal descent from the same ancestor but who cannot specify all of the actual links. The ancestor is genealogically so remote that he or she is often thought of as a mythical being, animal, or plant. Clans usually consist of a number of related unilineages. See totem.
-
cognatic
 descent
descent - tracing kinship through both the mother's and the father's ancestors to some degree. Cognatic descent occurs in four forms: ambilineal, bilineal, parallel, and bilateral descent.
-
collateral
 relative
relative - uncles, aunts, cousins, nephews, nieces and other consanguinal kinsmen beyond ego's main line of descent.
- consanguinity

- a socially recognized biological
descent link, such as between a woman and her father, aunt, or
daughter. Individuals who have a consanguinity relationship are
"consanguines"
 to each other. Consanguinity literally means
"with the blood", reflecting the old incorrect assumption that biological
inheritance is passed on through blood rather than DNA. See
affinity.
to each other. Consanguinity literally means
"with the blood", reflecting the old incorrect assumption that biological
inheritance is passed on through blood rather than DNA. See
affinity. -
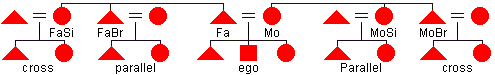
cross cousin

- one's father's sister's children or mother's brother's children. The gender of the children is not relevant in making this distinction. See parallel cousin.
-
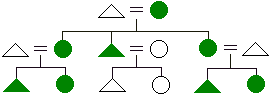
Crow
 naming system
naming system - a matrilineally based kin naming system in which siblings and parallel cousins of the same gender are given the same term of reference (5 = male and 6 = female) as are mother and mother's sister (2). Other people in ego's father's matrilineage are lumped across generations (1 = male and 3 = female), reflecting the comparative unimportance of the father's side of the family in societies using the Crow system.
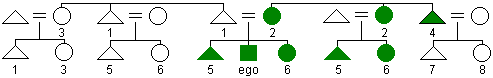
Back to Top
- D -
- descent

- socially recognized links between ancestors and descendants, such as the bond between children and their parents.
- descriptive kin naming system
- double descent
- see bilineal descent.
- dowry

- money, property, or other things of high value given by a bride's family to the groom, ostensibly to establish a new household. It is her share of the family inheritance. A dowry is, in a sense, the reverse of a bride price.
Back to Top
- E -
- ego
 (in a kinship diagram)
(in a kinship diagram) - the individual to whom all relationships are referred.
-
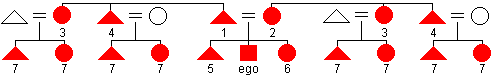
Eskimo
 naming system
naming system - a bilateral descent based kin naming system in which members of the nuclear family are given terms of reference based only on their gender and generation. Aunts (3) and uncles (4) are distinguished from parents (1 = father and 2 = mother) and separated by gender. The spouses of aunts and uncles may also be given these kin terms. All cousins are lumped together with one kin term (7) without regard to gender. No kin name distinction is made between uncles, aunts, and cousins with regards to side of the family.
Back to Top
- F -
-
family
of orientation

- see nuclear family.
-
family
of procreation

- see nuclear family.
- fictive
kinship

- a socially recognized link between individuals, created as an expedient for dealing with special circumstances, such as the bond between a godmother and her godchild. Fictive kinship bonds are based on friendship and other personal relationships rather than marriage and descent.
Back to Top
- G -
- gender

- sexual identity as male or female.
- genealogy

- the family history, or record of descent, of an individual from his or her ancestors.
- godparent
- a person who sponsors a child and assumes some parental responsibility for its upbringing. A godparent shares this responsibility with the "real" parents. A godparent is a fictive kinsman who may be either a godmother or a godfather to a godchild.
Back to Top
- H -
-
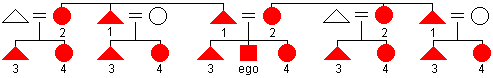
Hawaiian
 naming system
naming system - a kin naming system in which relatives are distinguished only by generation and gender. This results in just 4 different kin terms of reference. Ego's father and all male relatives in his generation are referred to by the same kin term (1). Likewise, ego's mother and all female relatives in her generation have the same kin term (2). All brothers and male cousins are linked by giving them the same kin term (3). Sisters and all female cousins are also referred to by the same term (4).
Back to Top
- I -
- in-law
- a person, other than a spouse, whose kinship relationship to ego is only through a marriage bond. Brother-in-law and mother-in-law are examples. In-laws are often considered to be relatives by societies following the Eskimo kin naming system. However, such affinal relatives are usually considered to be more distant in terms of kinship obligations and privileges than consanguinal ones.
-
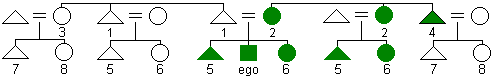
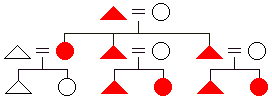
Iroquois
 naming system
naming system - a kin naming system in which the same term of reference is used for father and father's brother (1) as well as mother and mother's sister (2). Parallel cousins from both sides of the family are lumped together with siblings but distinguished by gender (5 = male and 6 = female). All cross cousins are similarly lumped together and distinguished by gender (7 = male and 8 = female).
Back to Top
- J -
Back to Top
- K -
- kindred

- a family group bound together by their kinship ties to one person. An individual's kindred consists of all of the people who are related to him or her through consanguinal ties and possibly affinal ones as well. That is, it includes one's biological relatives and sometimes spouses and in-laws.
- kin naming system
- a culturally defined set of rules for terms of address and reference to be used for specific categories of relatives. There are 6 different kin naming systems in use around the world: Eskimo, Hawaiian, Sudanese, Omaha, Crow, and Iroquois. Kin naming systems are also referred to as "kin terminological systems."
- kinship

Back to Top
- L -
Back to Top
- M -
-
matricentric
 family
family - a
nuclear
family in which there is no continuing adult male functioning as a
husband/father. This man is missing due to death, divorce, abandonment, or no
marriage having taken place. In such families, the mother raises her children more
or less alone and subsequently has the major role in their socialization.
Matricentric families are also referred to as being "matrifocused"
 .
. - matrilineage

- a multi-generational group of relatives who are related by matrilineal descent. Matrilineages usually consist of a number of related nuclear families descended from the same woman.
-
matrilineal
 descent
descent - unilineal descent that follows the female line. With this pattern, people are related if they can trace descent through females to the same female ancestor. Both males and females inherit membership in a matrilineal family line, but only females can pass it on to their descendants.
-
- moiety

- one of two unilineal divisions of an entire society. Moieties have reciprocal privileges and obligations with each other, such as providing marriage partners and assisting at funerals. The founding moiety ancestor is often so genealogically remote that he or she is now mythical. Societies with moieties usually consist of a few thousand people or less. Societies with phratries instead of moieties are often larger.
-
monogamy

- marriage of one woman to one man at a time. This is the most common marriage pattern around the world today. If remarriage is allowed following divorce or death of a spouse, the marriage pattern could be defined as being "serial monogamy."
Back to Top
- N -
- nuclear
 family
family - a family consisting of a man, woman, and their children. We are born into our "nuclear family of orientation" and we have children in our "nuclear family of procreation." Parents may think of themselves as being members of both of these families at the same time. See matricentric family.
Back to Top
- O -
-
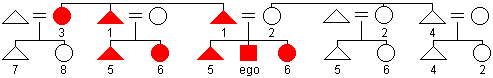
Omaha
 naming
system
naming
system - a patrilineally based kin naming system in which relatives are lumped together on the basis of descent and gender. Siblings and parallel cousins of the same gender are given the same term of reference (5 = male and 6 = female). Father and father's brother also have the same kin term (1). Other people in ego's mother's patrilineage are lumped across generations (2 = female and 4 = male).
Back to Top
- P -
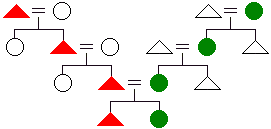
- parallel
cousin

- one's father's brother's children or mother's sister's children. The gender of the children is not relevant in making this distinction. With unilineal descent, parallel cousins are members of the same unilineage. See cross cousin.

- parallel
 descent
descent - the cognatic pattern of descent in which males trace their descent through the male line of their father and females through the female line of their mother. Unlike bilineal descent, every individual is a member of only one unilineage.
- pastoralists

- people whose economy is based on the herding of large domesticated animals, such as cattle, horses, sheep, or reindeer. Nomadic pastoralists travel with their animals in search of grass and water without a regular route. In contrast, transhumance pastoralists travel with their animals between specific traditional locations, such as summer mountain pastures and winter lowland pastures where they often have established villages.
- patrilineage

- a multi-generational group of relatives who are related by patrilineal descent. Patrilineages usually consist of a number of related nuclear families descended from the same man.
-
patrilineal
 descent
descent - unilineal descent that follows the male line. With this pattern, people are related if they can trace descent through males to the same male ancestor. Both males and females inherit a patrilineal family membership but only males can pass it on to their descendants. Also known as "agnatic descent."
-
- phratry

- a unilineal descent group consisting of a number of related clans. The phratry founding ancestor is so remote genealogically that he or she is usually mythical. Phratries are larger and more inclusive kinship groups than unilineages and clans.
Back to Top
- Q -
Back to Top
- R -
-
reciprocity
 (or reciprocal exchange)
(or reciprocal exchange) - a relationship between people that involves trading or exchange of gifts of goods, services, or favors. Inherent in reciprocal exchanges is the obligation to return a gift or comparable trade item in a culturally appropriate manner. Failure to do so is likely to end the reciprocal relationship. Reciprocity requires adequacy of response but not necessarily mathematical equality. Reciprocity is a common way of creating and continuing bonds between people.
Back to Top
- S -
- siblings

- brothers or a sisters.
-
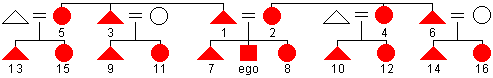
Sudanese
 naming system
naming system - a kin naming system in which kinsmen are not lumped together under the same terms of reference. Each category of relative is given a distinct term based on genealogical distance from ego and the side of the family. Also referred to as the "descriptive kin naming system."
Back to Top
- T -
- totem

- a mythical
clan
founding ancestor. Totem origins are so far back in time that they are often
believed to be non-human. Totems are used as symbols of clans. When they are
believed to be particular kinds of animals or plants, killing or eating them is usually
not allowed. Totems are also referred to as "totemic emblems"
 .
. - transhumance

- a variation of a pastoral way of life in which people migrate seasonally with their herds, usually from lowlands to highlands and back. Such movements are necessary for the year-round care of their animals upon which they depend. Transhumance is not nomadism since the cyclical migrations are between predetermined, traditional destinations.
Back to Top
- U -
- unilineage

- a multi-generational group of relatives who are related by unilineal descent. Unlike clans, phratries, and moieties, members of unilineages usually know the precise genealogical link to the founder. Unilineages usually consist of a number of related nuclear families. See also matrilineage and patrilineage.
- unilineal
 descent
descent - tracing kinship only through a single line of ancestors, male or female--that is, descent links are traced only through ancestors of one gender. See also matrilineal, patrilineal, and cognatic descent.
Back to Top
- V -
Back to Top
- W -
Back to Top
- X -
Back to Top
- Y -
Back to Top
- Z -
Back to Top
This page was last updated on
Tuesday, September 08, 2009.
Copyright 1997-2009 by Dennis O'Neil.
All rights reserved.
Illustration credits