The gender of a person who is represented by a triangle in kinship diagrams.
The gender of a person who is represented by a square in kinship diagrams.
In kinship diagrams, the term that is used to label the person to whom all kinship relationships are referred.
What an equals sign (=) represents in kinship diagrams.
marriage bond between a husband and his wife
What a vertical line represents in kinship diagrams.
bond of descent (e.g., parent-child bond)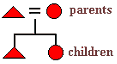
The general descent principle in which kinship is traced only through a single line of ancestors, male or female. Both males and females are members of a family, but descent links are only recognized through relatives of one gender.
The descent principle in which kinship is traced only through the male line. With this pattern, people are related if they can trace descent through males to the same male ancestor. Both males and females inherit family membership but only males can pass it on to their descendants.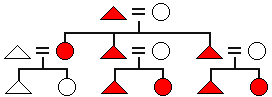
The descent principle in which kinship is traced only through the female line. With this pattern, people are related if they can trace descent through females to the same female ancestor. Both males and females inherit family membership but only females can pass it on to their descendants.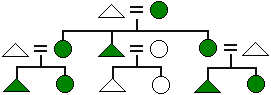
In societies using matrilineal descent, the man who most likely would have the formal kinship related responsibilities for a boy that European cultures assign to his father.
his mother’s brother (or maternal uncle)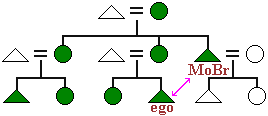
The family member from whom a woman will most likely inherit wealth, titles, or other status in a society with matrilineal descent.
The family member from whom a man will most likely inherit wealth, titles, or other status in a society with patrilineal descent.
The male family member from whom a man will most likely inherit wealth, titles, or other status in a society with matrilineal descent.
his mother’s brother (or maternal uncle)
The kinds of subsistence patterns of societies which are most likely to use unilineal descent. (Hint: all are societies with small populations that usually have more than adequate food supplies.)
materially rich foragers, small-scale farmers, and nomadic pastoralists
The general descent principle that about 60% of all societies used to trace descent until the early 20th century. (Hint: most of these societies had small numbers of people.)
The term for the variation of
cognatic descent in which both patrilineal and matrilineal descent lines are recognized. In this rare system, there are two direct ancestors in each generation—a male one and a female one.)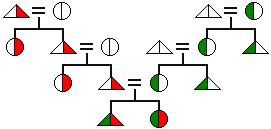
The descent system which results in only one direct ancestors in each generation.
The term for the variation of
cognatic descent in which men trace their ancestry through male lines and women trace theirs through female lines. (Hint: unlike bilineal descent, each individual is a member of only one descent group.)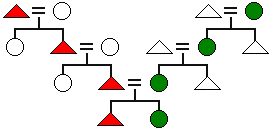
The term for the descent system in which individuals may select only one unilineal line to trace descent (male or female). Since each generation can choose which parent to trace descent through, a family line may be patrilineal in one generation and matrilineal in the next.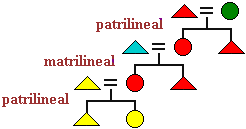
The cognatic descent system that is commonly used in North America and Europe today.
The descent system in which all male and female children are members of both their father's and mother's families.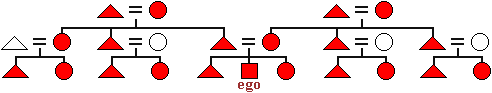
bilateral descent
The descent system that is used most commonly by large agricultural and industrial nations as well as by hunters and gatherers in harsh, relatively nonproductive environments such as deserts and arctic wastelands.
The number of direct ancestors in each generation back through time that potentially exist with bilateral or cognatic descent.
two parents and double the number of ancestors each generation back (i.e., 2, 4, 8, 16, etc.)
The descent system in which there are the least possible number of ancestors per generation—i.e., there is only one ancestor per generation.
unilineal (patrilineal or matrilineal) descent
The descent system in which there are the most possible number of ancestors per generation.
The descent system that can result in the largest number of possible descendants after 4 generations. Assume that in all descent systems that you are thinking of that everyone has exactly 4 children and that they all live to have 4 children. (Hint: there will be a total of 256 offspring with the descent system that has the most potential descendants.)