Glossary of Terms
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Select the first letter of the word you are seeking from the list above
to jump to the appropriate section of the glossary or scroll down to it
- A -
-
abdominal
wall defect

- a genetically inherited condition in which intestines and other abdominal organs protrude through the central abdominal wall. This must be corrected by surgery at birth.
- alleles

- alternate forms or varieties of a gene. The alleles for a trait occupy the same locus or position on homologous chromosomes and thus govern the same trait. However, because they are different, their action may result in different expressions of that trait.
- alpha-feto protein (AFP) sampling

- a routine diagnostic procedure for pregnant women to determine whether or not their fetuses have gross chromosomal anomalies. This screening procedure is also called maternal serum alpha-feto protein (MSAFP) testing. The testing is comparatively inexpensive but not as reliable as amniocentesis or chorionic villi sampling. With AFP sampling, blood is drawn from a pregnant woman in order to determine the amount of alpha-feto protein that has leaked into her system from her unborn child. Unusually high or low amounts of AFP relative to the stage of pregnancy indicate that there may be specific kinds of genetic defects. Specifically, it may indicate the likelihood of Down syndrome, neural tube defects, abdominal wall defects, and trisomy 18. Low AFP levels are associated with Down syndrome, while high levels are indicative of neural tube defects. The amounts of other diagnostic fetal chemicals (hCG and estriol) also are measured in expanded AFP screening or triple-screening.
- Alzheimer
syndrome

- a progressive, irreversible disease characterized by degeneration of brain cells that commonly result in severe loss of memory, the ability to think, and pay attention. There are also usually major changes in personality. Alzheimer syndrome most often occurs in late middle and old age. Genetic factors probably play a role since this syndrome is more common in some families.
- amniocentesis

- a diagnostic procedure for pregnant women to determine whether or not their fetuses have gross chromosomal anomalies. It involves sampling the liquid immediately surrounding a fetus within the amnion. This amniotic fluid is extracted through the mother's abdominal and uterine walls with a hypodermic needle. The amniotic fluid mostly contains fetal urine but also has millions of fetal skin cells that can be cultured to produce a karyotype. There is 99+% accuracy in diagnosing Down syndrome and most other gross chromosomal aberrations including neural tube defects such as spina bifida.
-
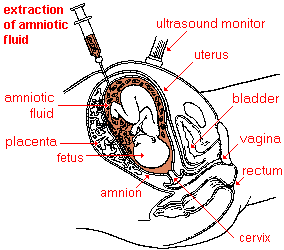
- amnion

- amniotic
fluid

- anencephaly

- the failure to develop a brain at the end of the spinal chord. This type of neural tube defect always causes the death of a fetus or newborn child.
- aneuploidy

- a chromosomal abnormality in which there is an addition or loss of chromosomes within a set (e.g., 23 + 22 or 23 + 24). Down syndrome is most often the result of this kind of error. See monosomy, trisomy, and polyploidy.
-
autism

- a neurodevelopmental disorder in children that prevents them from communicating normally and from relating normally with other people. Symptoms usually appear by age three.
- autoimmune
disorder

- any of several disorders in which one's antibodies attack his/her own body tissues. Lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and even common allergies are caused by such autoimmune reactions.
- autosomes

- any chromosome other than a sex chromosome. Human somatic cells have 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes.
Back to Top
- B -
- biopsy

- the process of removing a tissue sample from a living organism for diagnostic examination (e.g., chorionic villi sampling).
Back to Top
- C -
- cataracts

- impairments of vision caused by the lenses of the eyes becoming cloudy. Cataracts are common in elderly people. They may be inherited or caused by environmental factors.
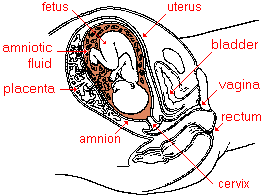
- cervix

-
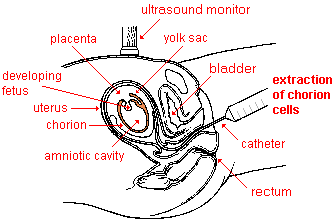
- chorion

- The membrane that develops around an embryo and contributes to the formation of the placenta. Later, as a fetus develops, the chorion fuses with the amnion. See chorionic villi sampling for an illustration.
-
chorionic
villi sampling
 (or biopsy
(or biopsy
 )
) - a diagnostic procedure for pregnant women to determine whether or not their fetuses have gross chromosomal anomalies. It involves collecting a small sample of chorion cells for karyotyping. The biopsy usually is done by inserting a small flexible plastic tube through the vagina and the cervix of the uterus to draw out a sample of chorion tissue. Alternately, the cells may be extracted with a hypodermic needle through the uterine wall, as in the case of amniocentesis. With CVS, there is approximately 98% accuracy in diagnosing Down syndrome and many other conditions due to gross chromosomal abnormalities. However, the accuracy in predicting neural tube defects is lower than with amniocentesis. Some sources refer to CVS as "chorionic villus sampling". "Villus" is the singular of "villi".
-
- chromatids

- one of two or more strands of a chromosome that are joined at a centromere.
- chromosomes

- thread-like, gene-carrying bodies in the cell nucleus. Chromosomes are composed primarily of DNA and protein. They are visible only under magnification during certain stages of cell division. Humans have 46 chromosomes in each somatic cell and 23 in each sex cell.
- crossing-over
- see recombination.
Back to Top
- D -
-
diabetes (diabetes
mellitus
 )
)
- an inherited metabolic disorder in which the pancreas does not produce enough of the hormone insulin. Symptoms include excessive urination, persistent thirst and hunger, as well as persistent fatigue and weight loss. Without treatment, this disease can be debilitating and even fatal.
- diploid
 number
number - referring to the full component of chromosomes normally found in somatic cells. In humans, the number is 46. See haploid number.
- DNA
 (deoxyribonucleic acid
(deoxyribonucleic acid
 )
) - a large organic molecule that stores the genetic code for the synthesis of proteins. DNA is composed of sugars, phosphates and bases arranged in a double helix shaped molecular structure. Segments of DNA in chromosomes correspond to specific genes.
- Down
syndrome

- a genetically inherited form of mental retardation usually resulting from the inheritance of an extra autosome 21. Down syndrome individuals also typically are short and stocky in build with short appendages. They usually have broad round faces, saddle-shaped nose profiles, and thick tongues that are often stuck out of their mouths. The incidence of Down syndrome children goes up rapidly with the age of the mother, particularly after 40.
Back to Top
- E -
- embryo

- the earliest stage of development of an unborn child. In humans, the embryonic stage lasts up till about the 8th week of pregnancy. Following, is the fetal stage.
-
epicanthic
fold

- a fold of skin over the inner corner of each eyelid. This is characteristic of normal East Asians (see photo on right). It is also typical of people with Down syndrome from any population in the world. The presence of epicanthic folds does not imply Down's.
- epilepsy

- a usually recurrent disorder of the brain characterized by abnormal electrical activity which causes mental and physical dysfunction. In serious cases, there are convulsions and unconsciousness when seizures occur.
- estrogen

- a class of feminizing hormones. Both men and women produce them, but females normally produce much more.
Back to Top
- F -
- false positive
- a test result that indicates a medical problem when there actually is not one.
- fertilization
- conception; the process of sexual reproduction by which the chromosomes from a sperm cell enter the nucleus of an ovum and combine with its chromosomes.
- fetus

- an unborn child during the later stages of pregnancy. In humans, an embryo usually becomes a fetus after the 8th week of gestation. Unlike embryos, fetuses have clearly recognizable physical characteristics of the species and gender.
- fragile-X
syndrome

- a relatively common genetically inherited abnormality of the X chromosome which results in mental retardation. Since it is an X-linked trait, males more often have it expressed in their phenotypes. Most fragile-X males have large testes, big ears, narrow faces, and sensory integration dysfunctions that result in learning disabilities. It is likely to occur 1 in 1000 births. Approximately 1 in 700 females are carriers of the gene for this trait.
Back to Top
- G -
- gametes

- reproductive cells--sperm or unfertilized ovum cells produced in the testes and ovaries of animals. Gametes are produced by meiosis. They normally have half the number of chromosomes found in somatic cells.
- genes

- units of inheritance usually occurring at specific locations, or loci, on a chromosome. Physically, a gene is a sequence of DNA bases that specify the order of amino acids in an entire protein or, in some cases, a portion of a protein. A gene may be made up of hundreds of thousands of DNA bases. Genes are responsible for hereditary characteristics in plants and animals.
- genotype

- gestation

- the period between conception and birth during which an unborn young is within its mother's uterus. Pregnancy is another word for gestation.
Back to Top
- H -
- haploid
 number
number - referring to the number of chromosomes in gametes. Human sperm and ova normally contain only 23 chromosomes, which is the result of the halving of chromosome pairs in meiosis. See diploid number.
- hernias

- protrusions of an organ through a tear in the wall of the surrounding structure (e.g., the protrusion of part of the intestine through the abdominal muscle and surrounding fascia tissue).
- homologous
 chromosomes
chromosomes - chromosomes that are paired during meiosis. Such chromosomes are alike with regard to size and also position of the centromere. They also have the same genes, but not necessarily the same alleles, at the same locus or location.
- hormones

- substances (usually proteins) that are produced by specialized cells and that travel to other parts of the body, where they influence chemical reactions and regulate various cellular functions. Hormones include the secretions of the endocrine glands that affect metabolism and behavior. Testosterone, estrogen, and insulin are examples of such hormones.
- hypodermic
 needle
needle - a hollow needle, connected to a syringe, used to either inject fluid materials into the body tissues or to extract blood or other fluids from the body. "Hypodermic" literally means "beneath the skin."
- hypothyroidism

- a disorder caused by the thyroid gland not producing enough hormones. Symptoms usually include a decreased metabolic rate which results in physical and mental depression, sluggishness, and puffiness.
Back to Top
- I -
Back to Top
- J -
Back to Top
- K -
- karyotype

- pictures of chromosomes cut out from a microphotograph of a cell and rearranged into homologous pairs according to size and other physical characteristics. The standardized arrangement of karyotypes allows researchers to discover if an individual is a male or female and if he/she has any gross chromosomal abnormalities.
- Klinefelter
syndrome

- a genetically inherited sex chromosome abnormality only affecting males. Genotypically, they are XXY or more rarely XXXY, or XXXXY. They have asexual to feminine body contours as well as breast enlargement and relatively little body hair. They are sterile or nearly so and their penis, testes, and prostate gland are small. Like metafemales, most Klinefelter syndrome men are an inch or so above average height. They usually have slight learning difficulties, especially with language. However, most are sufficiently ordinary in appearance and mental ability to live in society without notice. The frequency of Klinefelter syndrome has been reported to be between 1 in 500 and 1 in 1,000 male births. Males with Down syndrome sometimes also inherit Klinefelter syndrome.
Back to Top
- L -
- leukemia

- a class of cancers of the blood cells and blood-forming organs resulting in exceptionally high leukocyte (white blood cell) production. Other organs can become involved as well. Leukemia can be caused by some viruses, chemicals, and radiation. However, there also may be a genetic connection. For instance, individuals with Down syndrome have a much higher chance of developing leukemia.
- linked genes
- genes that are on the same chromosome and subsequently are inherited together as a package unless crossing-over separates them.
Back to Top
- M -
- medical syndrome
- see syndrome.
- meiosis

- cell division in specialized tissues of ovaries and testes which results in the production of sperm or ova. Meiosis involves two divisions and results in four daughter cells, each containing only half the original number of chromosomes--23 in the case of humans. These cells can develop into gametes. See mitosis.
- metafemales

- a genetically inherited sex chromosome abnormality only affecting females. Metafemales inherit three X chromosomes--their genotype is XXX. As adults, these individuals are usually an inch or so taller than average with unusually long legs and slender torsos. They have normal development of sexual characteristics and are fertile. They may have slight learning difficulties and are usually in the low range of normal intelligence. They tend to be emotionally immature for their size during childhood. None of these traits prevent them from being socially accepted as ordinary women. This type of chromosomal abnormality is apparently rare and little is known about it. However, the frequency is approximately 1 in 1,000 female infants and it may be more common when the mother is older. Metafemales are also called "triple-X females."
- miscarriage
- mitosis

- the simple cell division process that occurs in somatic cells. One cell divides into two offspring cells that are identical to each other in their chromosome complement. Mitosis produces cells with diploid numbers of chromosomes--46 in the case of humans. See meiosis.
- Mongoloidism

- a now rejected alternate term for Down Syndrome.
- monosomy

- the form of aneuploidy in which there is only one chromosome instead of the usual two homologous chromosomes of each type. Conceptions with autosomal monosomies die before birth.
- mosaicism
 (mosaic
(mosaic
 )
) - a genetic pattern in which an individual has two distinct cell groupings--one with normal cells and another with a genetic problem. For instance, some people with Down syndrome produce both normal somatic cells and cells with an extra chromosome 21. Usually, this mosaic pattern results in a lessening of symptoms.
- mutagen

- an agent that can cause a mutation to occur. Various kinds of chemicals, viruses, and radiation have been identified as mutagens.
- mutation

- an alteration of genetic material such that a new variation is produced. For instance, a trait that has only one allele (A) can mutate to a new form (a). This is the only mechanism of evolution that can produce new alleles of a gene. Technically, mutation refers to changes in DNA bases as well as changes in chromosome number and /or structure. See mutagen.
Back to Top
- N -
- neural
tube defects

- defective developments of the brain or spinal cord. By the mid embryonic stage (5 weeks in humans), a neural tube extends from the top of the head to the lower end of the spinal column. Later, this tube becomes the brain and spinal chord. Spina bifida and anencephaly are examples of neural tube defects.
- nondisjunction
errors

- a mechanical error that can occur during meiosis and mitosis. Specifically, members of a pair of homologous chromosomes move to the same pole rather than opposite poles. In meiosis, this can result in one gamete receiving two of the same type of chromosome and another receiving none of this type. Nondisjunction is a cause of gross chromosomal abnormalities.
Back to Top
- O -
- ocyte

- ogenesis

- osteoporosis

- a bone disorder in which there is a progressive reduction in bone density resulting in brittleness and increased porosity. People with osteoporosis are at a high risk for bone fractures. This disorder is most commonly found among post-menopausal women. However, it also occurs at a high frequency among men who have low testosterone levels (e.g., men with Klinefelter syndrome).
- over expression
- the abnormal expression of a trait in the phenotype of an individual resulting from the presence of extra chromosomes or copies of the genes responsible for the trait. For example, Down syndrome traits are likely the consequence of inheriting three chromosome 21's instead of the usual two. Apparently, the genes on the extra chromosome are also expressed.
- ovulation

- ovum
 (plural
(plural
 ova)
ova)
Back to Top
- P -
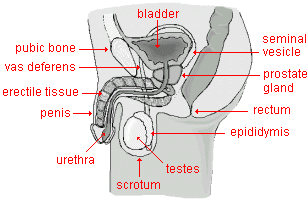
- penis

- the external male sex organ through which urine and semen pass. The penis mostly consists of the urethra and three cylindrical bodies of erectile tissues. See prostate gland for illustration.
- phenotype

- the observable or detectable characteristics of an individual organism; the detectable expression of a genotype.
- placenta

- an organ in the uterus of a mammal that develops from the chorion of an embryo during gestation. The placenta is connected to an unborn child by the umbilical cord. The placenta provides oxygen, nutrients, and antibodies for a fetus. Following birth the placenta and umbilical cord are naturally expelled from the uterus as the "after birth." See cervix for illustration.
- polyploidy

- a chromosomal abnormality in which there are extra complete multiples of chromosome sets (e.g., 23 + 23 + 23). Polyploids are rare among animals but common in plants. A mosaic polyploidy (with only some ployploid cells) is the common animal form. See aneuploidy.
- postmenopausal

- after the period in a woman's life when her ovulations and menstruations have reduced in frequency and finally stopped altogether--i.e., after menopause. Menopause usually takes place between the ages of 45 and 55.
- primary o�cyte
- see o�cyte.
- prostate
gland

- a gland surrounding the urethra at the base of the bladder. It secretes most of the seminal fluid that is expelled with sperm cells during ejaculation.
- puberty

- the stage of maturation of an individual when secondary sexual characteristics begin to develop and sexual reproduction first becomes possible. These changes are genetically controlled and triggered by hormones.
 |
Back to Top
- Q -
Back to Top
- R -
- recombination
- the exchange of genetic material (DNA) between homologous chromosomes at the beginning of meiosis. This results in sperm and ova with greater genetic diversity. Specifically, a portion of a chromosome is broken and reattached on another chromosome. Recombination is also referred to as crossing-over.
- rickets
disease

- a disease of the skeletal system in which the bones are softened and often bent as a result of vitamin D deficiency in the diet that hinders the normal development of bones and teeth. Rickets most frequently affects malnourished children.
Back to Top
- S -
-
schizophrenia

- a severe mental disorder characterized by disorganized, faulty perceptions of reality that create difficulty in relating to other people. Schizophrenics often experience intense hallucinations, delusions, and/or psychotic defenses.
- secondary o�cyte
- see o�cyte.
- sex cell
- a gamete, either a sperm or an ovum. Sex cells are produced by the meiosis process. See somatic cell.
- sex chromosome
- the X and Y chromosomes which are responsible for determining whether an individual is a male or a female. Normal males inherit an X from their mother and a Y from their father. Normal females get an X chromosome from both parents. See SRY gene.
- sex-linked
- referring to a gene that is part of a sex chromosome. Since all of the genes on a chromosome are inherited as a package, they are essentially linked together.
sickle-cell trait
![]()
a genetically inherited recessive condition in which some or all of the red blood cells are abnormally distorted to a sickle shape. Symptoms include pain and severe anemia as well as heart, lung, and kidney problems. People who are heterozygous for this trait rarely have these debilitating and ultimately fatal problems but do have a high degree of immunity to malaria. Sickle cell trait is at its highest frequency among Central African populations and among people whose ancestors came from that region. Sickle-cell trait is often referred to as sickle-cell anemia.
- somatic
cell

- basically, all the cells in the body except those directly involved with reproduction. Most cells in multicellular plants and animals are somatic cells. They reproduce by mitosis and have a diploid number of chromosomes. See sex cell.
- sperm

- a male sex cell or gamete.
- spermatogenesis

- spina bifida

- a neural tube birth defect in which there are malformations of vertebrae and the protrusion of the spinal cord. This can result in paralysis of the legs, loss of bowel and bladder control, and "water" on the brain (hydrocephaly). Spina bifida requires surgical correction.
-
SRY gene

- sex-determining region Y gene. A gene on the Y chromosome which, if present and functioning, causes the undifferentiated sex organs of an animal embryo to become testes. These then produce the hormone testosterone which, in turn, causes the development of masculine physical traits.
- syndromes

- a number of conditions that occur together and characterize a particular disease or condition (e.g., Klinefelter syndrome).
Back to Top
- T -
- testes
 (or testicles
(or testicles
 )
) - the two male sex organs within the scrotum. Testes produce the hormone testosterone and sperm cells. See prostate gland for illustration.
- testosterone

- thyroid

- the large gland in the neck next to the trachea that secretes the hormone thyroxine, which regulates body growth and metabolism.
- translocation
- a structural modification of a chromosome in which a portion of a chromatid is broken off and attached to a different location on that chromosome or on another chromosome. This occurs as a result of crossing-over.
- triple-X female
- see metafemale.
- trisomy

- the form of aneuploidy in which there are 3 chromosomes instead of just 2 for a specific homologous pair. An example is the common form of Down syndrome in which there are 3 chromosome 21's. Most fetuses with autosomal trisomies die before birth.
-
trisomy 18

- a rare chromosomal abnormality in which there is a trisomy of chromosome 18. This inherited condition is also called Edward's syndrome. It is characterized by severe mental retardation, a small head with malformed ears set low, and a face with a pinched appearance. Other likely defects include a cleft palate, webbed hands, missing thumbs, clubfeet, as well as heart and genitourinary defects. Individuals with trisomy 18 usually die within a few months after birth.
- trisomy
21

- see Down syndrome.
- Turner
syndrome

- a genetically inherited sex chromosome abnormality only affecting females. Women with Turner's only have one X chromosome--their genotype is X0. These individuals are short in stature, averaging 4'7" and have distinctive webbed necks (i.e., extra folds of skin). They have exceptionally small breasts and generally lack secondary sexual characteristics. Their ovaries do not develop normally and they do not ovulate. They are in a sense postmenopausal from early childhood and are sterile. In some individuals, there is slight mental retardation. Turner syndrome is rare--current estimates of its frequency range from 1 in 3000 to 1 in 5,000 females.
Back to Top
- U -
- ultrasound monitoring
- the use of high frequency sound to form an image or picture of internal organs for immediate medical diagnostic purposes. The Ultrasonography device transmits sound waves directly into the body and then accurately records the amount of time for echoes to return to a receiver, much like radar. The sound waves used are at frequencies above the threshold of human hearing--e.g., 20,000 vibrations per second.
- uterus

Back to Top
- V -
- vagina

- variable penetrance
- the expression of a genetically inherited trait in different forms or degrees in different people. For example, the alleles for the Down syndrome genes may cause an effect in the phenotype of some individuals but not others. As a result, there is considerable variability within the Down syndrome population in regards to susceptibility to the characteristic unpleasant medical problems.
Back to Top
- W -
Back to Top
- X -
-
X-linked

- referring to a gene that is carried by an X chromosome. See sex-linked gene.
- XXX
syndrome

- see metafemale.
- XYY
syndrome

- a genetically inherited sex chromosome abnormality only affecting males. Men with XYY syndrome inherit an extra Y chromosome--their genotype is XYY. They are usually quite tall (i.e., above 6 feet) and generally appear and act normal. During adolescence, they frequently have severe facial acne. They are usually fertile and lead ordinary lives as adults. Many, if not most, are unaware that they have a chromosomal abnormality. The frequency of XYY syndrome is not certain due to statistical differences between different studies of this condition. It may be as common as 1 in 900 male births to as rare as 1 in 1,500 or even 1 in 2,000.
Back to Top
- Y -
-
Y-linked

- referring to a gene that is carried by a Y chromosome. See sex-linked gene.
Back to Top
- Z -
- zygote

- a "fertilized" ovum. More precisely, this is a cell that is formed when a sperm and an ovum combine their chromosomes. A zygote is the beginning of a multicellular plant or animal, such as a human.
Back to Top
Copyright
1997-2012 by Dennis
O'Neil.
All rights reserved.
illustration
credits
